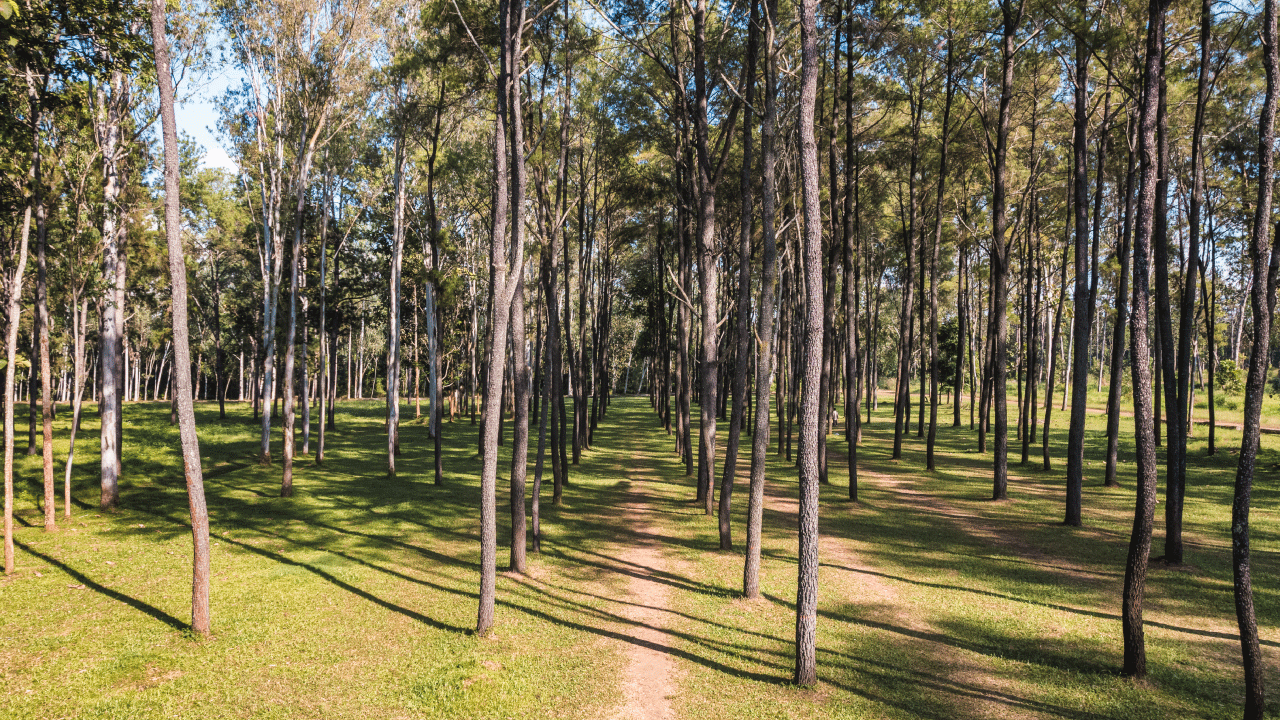
The installation of solar panels in forested areas inevitably involves the alteration of the natural environment. The clearing of trees and vegetation is a major concern, as it can lead to the loss of natural habitats and affect local biodiversity. Land preparation can also alter the soil structure, affecting its ability to retain water and nutrients, which could have long-term consequences for the ecosystem. In addition, local wildlife may be affected by the loss of their natural habitat. Species that depend on forests for food and shelter may be forced to move, which could alter their migration patterns and behaviour.
Despite these challenges, there are several strategies that can minimise the environmental impact of installing solar panels in forested areas. One of the most effective practices is revegetation with native species after installation. This not only helps to restore the natural habitat, but can also improve soil quality and promote biodiversity. The creation of ecological corridors is another important measure. These corridors allow local wildlife to move freely between fragmented habitat areas, reducing the impact of vegetation loss. In addition, the installation of nest boxes and insect hotels can provide shelter for birds and pollinators, helping to maintain ecological balance.
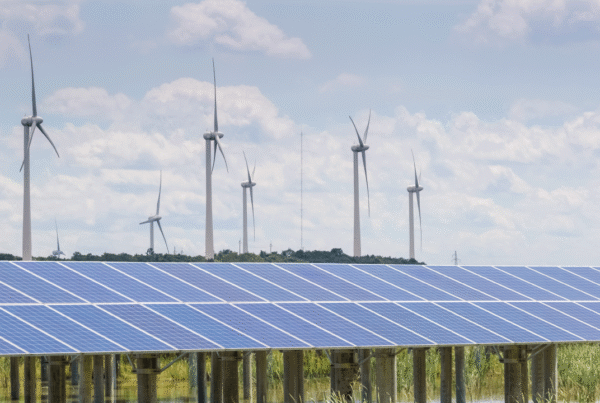
Despite the initial impacts, solar energy offers many long-term environmental benefits. By generating electricity without greenhouse gas emissions, solar panels contribute to a reduced carbon footprint. This is crucial in the fight against climate change, as it helps to reduce the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere. In addition, solar energy reduces our dependence on fossil fuels, which are finite and have a considerable environmental impact. By investing in solar energy, we are investing in a sustainable and renewable energy source that can meet our energy needs without compromising the environment.
In some regions, solar panels are being integrated with agriculture in an approach known as ‘agrovoltaics’. This allows solar panels and crops to coexist on the same land. The panels provide shade, which can reduce water evaporation and protect crops from extreme temperatures.
Installing solar panels in forested areas presents challenges, but also offers significant opportunities to move towards a more sustainable future. With the implementation of appropriate mitigation measures and a balanced approach, it is possible to minimise environmental impacts and maximise the benefits of solar energy. In doing so, we can contribute to the conservation of our natural ecosystems while harnessing a clean, renewable energy source.
——————————————–
Find out more news about the renewable energy sector on the Univergy Solar blog.